A spread order is a trading strategy which involves going long (buying) in one contract whilst shorting (selling) another contract of the same or different underlying.
Spread orders are normally executed in the Futures segment and look at capitalizing on the difference between the prices of the executed legs referred to as the "Spread".
Types of Spread Trades:
1) Calendar Spread: Involves entering into long & short position of the same underlying asset with 2 different expiry periods.
For example: Assume Reliance July futures with an expiry date of 30 July 2020 is trading at 1800 and August futures dated 27 August 2020 trading at 1900. You feel that this difference of 100 points between both the months is quite a bit and this will reduce to 60 points in the next few days, how do you profit from this idea? The idea is to profit without taking any naked directional risk, i.e., immaterial of the market going up or down, you should be able to profit if this difference between both the futures reduces from 100 to 60 points.
This situation can be used to implement Calendar spread in two different orders:
- Buy Reliance Futures 30 July 2020 at 1800
- Sell Reliance Futures 27 August 2020 at 1900
When the difference is lesser than 100 points, you make profits, and if the difference is more than 100 you make losses.
Below are the steps involved in placing a spread order from TTexe platform:
- Spread order can be found under Market > Spread Order as given below:
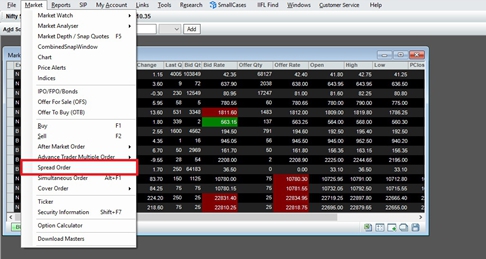
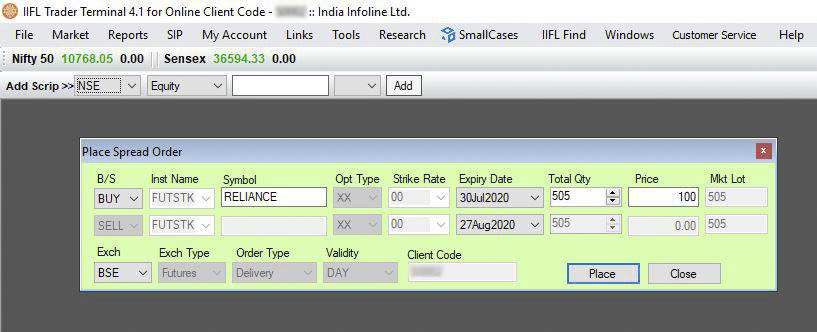
- User can then go long (buy) on one contract and short (sell) on other contract by specifying appropriate strike price and underlying price of the security.
In the image below, we can see that Reliance Futures July is buy and Reliance Futures August is sell. The difference in points is given in price as 100. A standard market lot size is 505 units.
Benefits:
- Hardly any market risk
- Margin requirement to setup a calendar spread is very less
For example: The margin required for 1 lot of Nifty is around INR 1.45 lakhs, so in case you have 2 lots the margin requirement should ideally be INR 2.9 lakhs.
But because this is a calendar spread the margin requirement for both the positions together due to the reduced risk is only INR 20000 and not INR 2.9 lakhs.
2) Inter commodity spread: Trading and trying to cash in on the difference between 2 closely derived Commodity contracts.
For example: A 'Crack Spread' which involves purchasing crude oil futures and taking an offsetting position by refined products of crude oil like gasoline, diesel etc
